Skin cancer
Skin cancer is one of those topics that many people are not over concerned about until it touches you personally, or someone nearest or dearest to you, and only then do you go out and obtain more knowledge. Fast!
Annually, there are more than 1.5 million new cases being recorded, with one death every hour. Although these statistics are really scary, once more knowledge is acquired, the fear is minimized and it becomes more obvious how much more efficiently we can protect not only ourselves, but our family, friends, and loved ones.
Skin cancer varieties
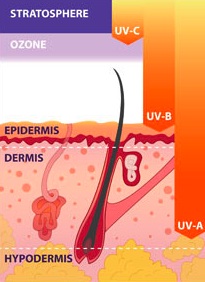
Skin cancers are all found within the epidermis - the outermost layer of the skin. Beyond this, they are all distinguished by their occurrence within the epidermis.
The two most common forms of this cancer, also known as non-melanoma cancers, are:
Other non-melanoma cancers include:
- Kaposi's sarcoma
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- cutaneous lymphoma
Melanoma is less common than all of these, but it is the most serious and the most fatal.
Of all the different cancers diagnosed, skin cancer collectively is the most common, including lung, breasts, colorectal, and prostate cancer.
Melanoma skin cancer
As the worst type of cancer of the skin you can develop, melanoma attacks the skin and quickly metastasizes (spreads or grows) to invade and attack the rest of the body, including internal organs.
If it isn't diagnosed early in order to stop the growth, a melanoma can ultimately prove to be fatal.
Squamous cell carcinoma
A type of cancer that originates in the squamous cells within the tissues in the middle of the epidermis, the squamous cell carcinoma is also sometimes called Bowen's disease.
These cancer cells can also be found in the digestive tracts, the lining of hollow body organs, and the respiratory passages.
Those with light-colored skin are more prone to getting this type of cancer. Symptoms include rough, red bumps on the face, ears, scalp, and the back of the hands.
Often sore and tender to the touch, these bumps can metastasize to other parts of the body, which is why it is necessary to be attentive to these kinds of cancer and not ignore them.
There are various treatments that can be done, depending on their severity. The most common treatments are surgical removal of the tumor, radiation therapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells, and a procedure called curettage and desiccation. This last procedure involves scooping out the squamous cell carcinoma and using an electric current to kill the leftover cancer cells as well as control the bleeding.
Basal cell carcinoma
A type of cancer that causes damage by growing and invading surrounding tissues within the body, the basal cell carcinoma takes the form of a small, dome-shaped bump, which is covered by small blood vessels.
These bumps can appear on your back or chest and often look like patches of dry, raw skin. Over a period of a few months or sometimes years, the bumps continue to grow and/or spread.
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma is pretty much the same as that for squamous cell carcinoma.
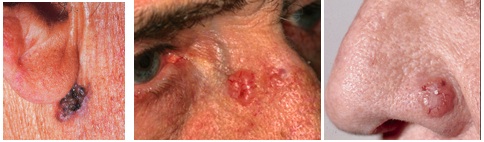 Some examples of Basel Cell carcinomas
Some examples of Basel Cell carcinomasSkin cancer protection:
Basal cell carcinoma and Squamous cell carcinoma seem to be undisputed as cancers directly aligned with sun damage.
Melanoma, however, being the one that is potentially fatal, is not indisputably caused through sun damage.
However, Basel cell and Squamous cell carcinomas can start a process that leads to Melanomas.
So protecting yourself when in the sun by using a broad-spectrum sunscreen or by wearing UPF clothing can help to prevent growth of Basel or Squamous cell carcinomas, which indirectly protects you from Melanomas.
Skin cancer alerts:
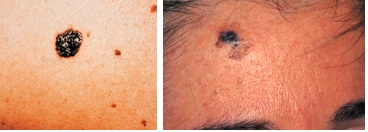 Some examples of quite obvious melanomas
Some examples of quite obvious melanomasBecause all 3 types of skin cancer occur within the epidermis, it makes them relatively easy to detect. Basically, look out for any of the following abnormal behaviors on your skin:
- New - something that you haven't noticed before
- Different - when compared to all your other moles or freckles
- Changing shape or form or texture - any change in an existing wart, mole, freckle or skin lesion
- Not healing - a sore that just will not heal
Noticing any of the above can be indicative of either Basel or Squamous cell growth. However, Basel cells grow very much more slowly than Squamous cells and so progress can be quite different.
Skin Cancer Risk factors

The sort of things you should be aware of that make you or your family more susceptible to these cancers include:
- Skin type: The more melanin you have the darker your skin will be. Melanin is our natural inbuilt defense against UV radiation, whereby it absorbs the UV radiation and dissipates the energy as harmless heat, thus preventing the UV rays from damaging the DNA. Thus, the more melanin we have in our skin, the better we are able to naturally defend ourselves from any sun damage. Skin cancers are therefore more common in people with light-colored skin, hair, and eyes.
- Family history of skin cancer: Your genetics seem to play a large part, so having a family history of melanoma increases the risk of developing cancer.
- Age: Non-melanoma skin cancers are increasingly common after age 40 but some of the damage can be done at a very early age and only noticed much later on.
- Overexposure to the sun: Sunburn is the result of having been exposed to too much sun without sufficient protection, resulting in damage to the UVA. This is considered to be the main cause of many skin cancers.
- Using sunscreens with no UVA protection: If you protect yourself using a sunscreen with only UVB (SPF) protection you effectively allow the UVA rays a longer time to do their damage. You are actually better off wearing no sunscreen at all than one with only UVB protection, or one with very little UVA protection.
Approximately 5% of the solar light reaching the earth's surface consists of UV (Ultra Violet) rays. Most of this light is skin penetrating UVA radiation. This is what causes the real damage.
However, UVB rays, the fraction that causes sunburn, makes up just 4% of this UV light. It is also only these UVB light rays that enable our skin, in a photosynthesis type process, to create Vitamin D. Amongst other things, Vitamin D provides protection against many forms of cancer.
A third fraction, the UVC rays, are filtered out by the atmosphere (ref Diffey 2002)
No-one is excluded from skin cancer risk.
Besides all of the above, it can develop in the young, the healthy, the dark skinned, and even the "never go in the sun" people. UVA rays will penetrate glass, so those who stay indoors or sit behind a car's glass windows, can also be exposed to potential harm.




New! Comments
Have your say... please leave me a comment in the box below.