Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant skin tumor, especially in people with pale skin origins, but it is only very rarely life-threatening. Statistics reveal that 1 person in 1,000, or 0.1%, of people who have this skin cancer, will die from it.
Usually caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet light, (either from the sun's UV rays, or tanning beds), it is not considered life threatening.
However, basel cell carcinoma can destroy the skin and it's surrounding tissues, including impacting on important things such as nerves or muscle tissues. Left to do it's thing unimpaired, it can cause significant damage, including cosmetic disfigurement, most especially on the face.
How does basal cell carcinoma develop?
Skin cancer is divided into two major groups:
- non-melanoma
- melanoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of non-melanoma skin cancer, and is the most common form of cancer in the world today. According to the American Cancer Society, 75% of all skin cancers in the USA are basal cell carcinomas.
Skin cancer develops when the division of skin cells gets out of control. This can lead to a malignant tumor. ie cancer. The affected areas can be flaky or dark in color, and sometimes distinctly raised, too. Skin cancer can develop from moles, birthmarks or lentigines, but most of them will remain harmless.
The skin's layers
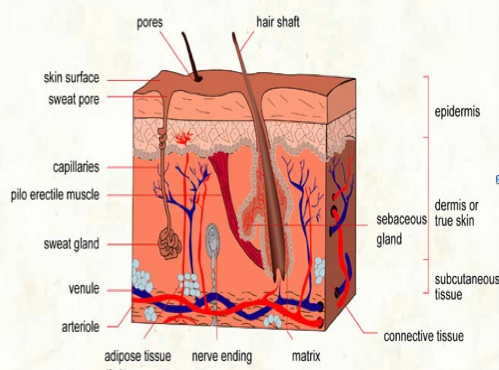 skin layers
skin layersOur largest organ, the skin, provides protection for the body from the weather conditions such as rain and dampness, or hot and cold, but also from the invasion of germs and toxic substances. It consists of three layers:
- Epidermis: the outermost layer of the skin made up of different cell sublayers
- Dermis: the middle layer of the skin, which contains sweat, scent and sebaceous glands, nerve fibers, blood and lymph vessels as well as hair roots
- Subcutaneous layer (hypodermis): lower layer of the skin, which consists mainly of fat and connective tissue
Basal cell carcinoma starts in the top layer of the skin called the epidermis. It grows slowly and is painless. It almost never spreads, but, if left untreated, it may grow into the surrounding tissue as well as bone.
Basal cell skin cancer used to be more common in people over the age of 40, but is now often diagnosed in younger people.
It is usually found on the sun exposed parts of the body like the face, neck, head and ears. Untreated lesions can slowly eat away the surrounding skin and hence they are also known as "rodent ulcers".
Basel cell carcinoma symptoms
Basal cell carcinoma may look only slightly different than normal skin. The cancer may appear as a skin bump or a growth that is:
- Pearly or waxy in feel
- White or light pink, or flesh-colored or brown in colour
- In some cases the skin may be just slightly raised or even flat
Some other signs include:
- A skin sore that bleeds easily
- A sore that does not heal
- Oozing or crusting spots in a sore
- Appearance of a scar-like sore without having actually been injured
- Irregular blood vessels in or around a spot
- A sore with a depressed, or sunken, area in the middle
Basel cell carcinoma tests
The same type of skin cancer can look very different from one person to another, which makes it hard to look at a visual picture and tell if it looks the same as something you are concerned about.
The best bet if at all unsure, is to ask your doctor or dermatologist to check your skin and look at the size, shape, color, and texture of any suspicious areas.
If skin cancer is considered a possibility, a biopsy may be requested. This requires that a piece of skin be removed from the area and examined under a microscope. This must be done to confirm the diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma or other skin cancers.
Skin biopsies are performed in many different ways and the exact procedure will depend on the location of the suspected skin cancer.
Basel cell carcinoma examples...
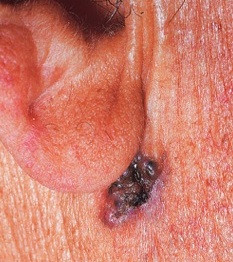
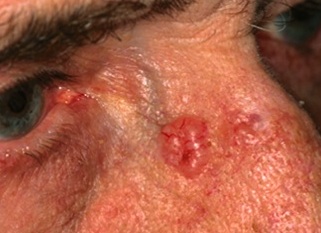
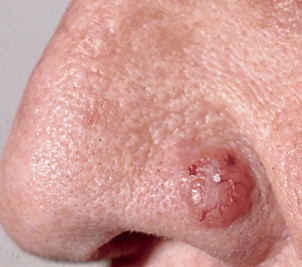
Basal cell carcinoma treatments include
- Surgical removal.
The commonest treatment for Basel Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is surgery. This is traditionally achieved by surgical excision (SE) which involves cutting away the BCC growth, along with the surrounding margin of normal appearing skin, to ensure complete removal of the cancer and to reduce the risk of recurrence.
If any residual BCC is left at the edge of the excision, more skin will be excised from only the area indicated by using the colour coding, and examined under the microscope. This process is continued until all the BCC is removed. This ensures complete tumour removal and spares normal, unaffected tissue in the other directions.
Another type of surgery is Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS). This involves the removal of the skin tumour after colour coding the edges. This is then examined under the microscope straight away to see if all the BCC has been removed.
This is considered the better alternative for treatment of certain types of BCC arising in the eyelids because it has the highest chance of curing the disease and minimises the size of the defect that needs to be repaired. - Radiotherapy. Also a very effective and together with surgical removal the most effective for high risk facial basal cell carcinoma.
- Cryotherapy (freezing). Cryotherapy, while convenient and less expensive, does not have a higher cure rate.
- Phototherapy (light therapy). Photodynamic therapy appears to be useful in the shortterm, especially for people who wish to avoid scarring. However, longterm followup is needed.
- Creams. Early results for imiquimod cream are very promising for superficial basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma references:
Advanced Basel cell Carcinoma: Understanding a Complex Disease




New! Comments
Have your say... please leave me a comment in the box below.