Sunburn
Not only is it extremely uncomfortable, if your skin gets a really bad sunburn it is downright dangerous. In the extreme, third degree burns can even require hospitalisation and the healing of your skin can take weeks! Never mind the very real danger of skin cancer.
The sun's UV (ultraviolet) rays provide so many wonderful qualities, but not knowing how best to manage your exposure to them, can lead you into trouble.
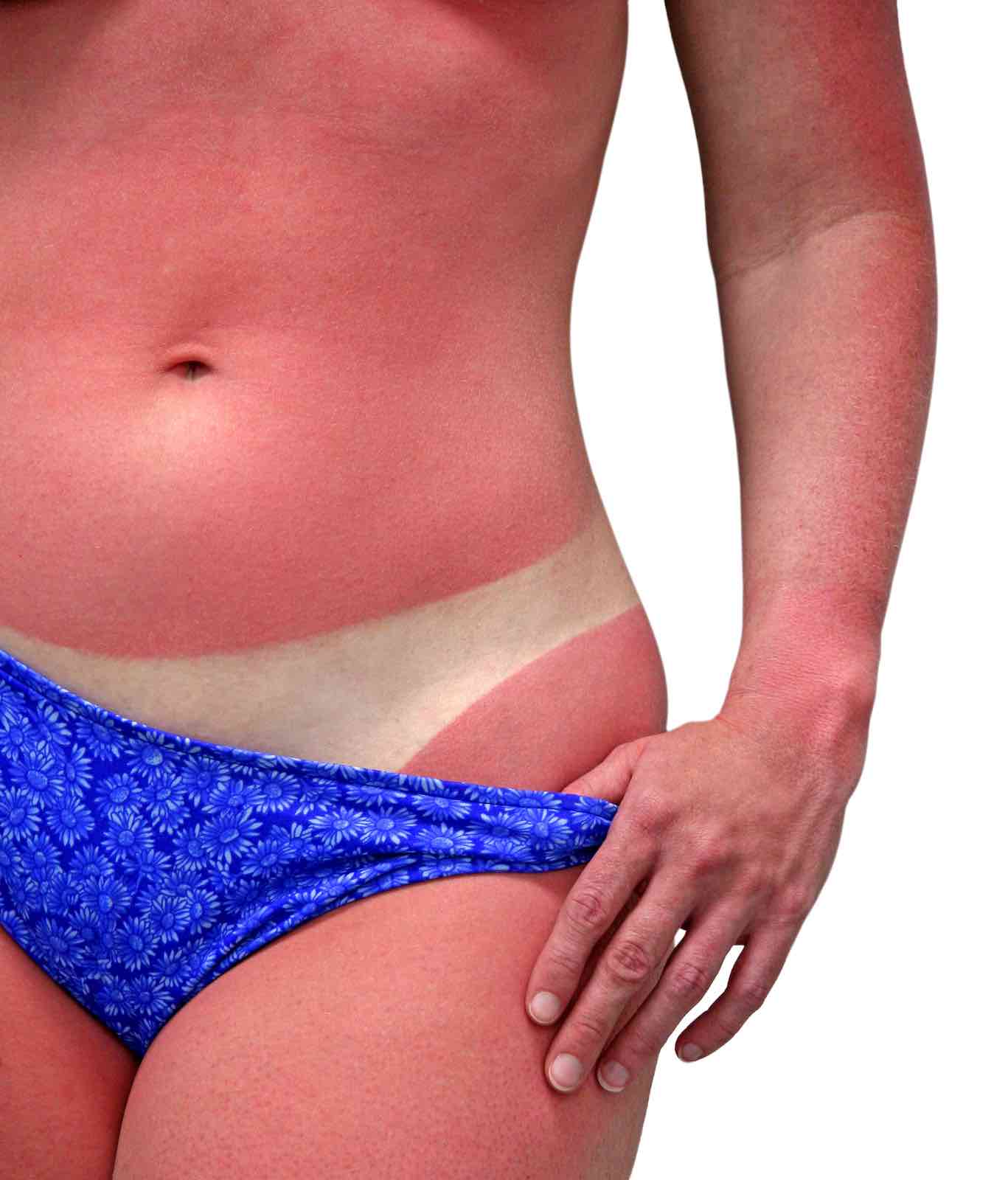
So what is a sunburn?
|
For us humans, the sun is both beautiful and life giving, but it's also powerful and if not treated with respect, dangerous. While it lights our day and provides essential life giving energy, sunlight can be harmful to human skin, regardless of your skin colour. The earth's atmosphere blocks much of the harmful UV light, but burning of your skin will occur when the UV rays from the sun are allowed to penetrate through your skin, causing inflammation. Depending on your skin type, a moderate exposure to the ultraviolet radiation will create a slight red blush to the skin, but exposure beyond your skins' capabilities will result in an attempt to heal the skin with raised blisters, and a message from your body telling you that it is not happy! ie. serious pain. Eventually, when the skin has done what healing it can, there will be a peeling of the dead skin layers. If not too deep a level of damage, the peeling will be light. If you experienced any deep level burns, the skin will most likely peel off in thick layers and possibly cause skin scarring. |
As the suns' rays penetrate the skin, they break down collagen and elastin, which are the two main structural components of the skin. This results in the wrinkled, sun-damaged skin look that's really not desirable.
This can go even further when the sun damages the DNA of the exposed skin cells. These cells then release enzymes that excise the damaged parts of the DNA and encourage the production of replacement DNA. This is where the process can go wrong and result in skin cancer.
At the same time, the production of melanin increases, which causes the skin to darken. Melanin is a pigment that gives skin its color, but also acts as a barrier to further damage by absorbing the ultraviolet light. Effectively, this darkened 'suntanned' skin is its natural response to protect itself.
Extra diligence in the sun is required for:
- Light-skinned people, who generally lack sufficient melanin protection so are much more open to getting their skin burnt
- Infants not yet melanin seasoned through exposure to the sun
- People who have an increased photosensitivity through certain diseases or the drugs they take
Symptoms and Effects of Sunburn
So if tanning is the skin's natural, defensive reaction to getting too much sun, is a sunburn much to fuss about? Not all burns are the same of course, but the damage is done regardless.
If you are someone with a skin that can endure the sun's rays reasonably well, you may find you can be in the sun for an hour or more and not get burnt, whereas those with very fair skin may get burnt within no time at all. But the attraction to be in the sun can blur the message the skin is trying to send. I have seen many a tourist who just can't resist the sunshine and even though I can almost see their skin turning red before my eyes, they won't leave the sun and seek shade!
The most common symptoms of the skin include:
- a hot, redness
- swelling
- tender or painful on touching
- blistering
- peeling
Unfortunately these symptoms only occur a few hours after being in the sun. Invariably this means that you sit out there in the sun believing you are not getting burnt and only find out a few hours later just how burnt you actually are!
Not only is it painful and unsightly, but every time you get sunburnt, you put yourself at risk of certain complications and the related skin diseases. These include:
- dry, wrinkled, aged skin
- liver spots
- actinic keratoses
- skin cancers
Treatment for Sunburn
Depending on how burnt you actually are, there are different ways to deal with your burns. You cannot really undo the physical damage done when you have got burnt, but you can assist the skin to recover and possibly even help reverse DNA damage.
Sometimes it may take several days for the skin to begin it's healing process, although it may take 12 to 24 hours after sun exposure to know the full extent and severity of the sunburn, and several days or more for your skin to begin to heal.

In the meantime, the following effective treatments will simply help to ease your discomfort:
- Keep it cool
The first best thing is a cool bath or shower or even cold compresses applied to the affected areas - Keep it Moist
Apply moisturizing gels or creams, especially those containing Aloe Vera or Aloe Ferox, as it helps soothe the redness and offers some temporary relief, as well as guarding against infection. You can even use the leaf direct from the garden - break off a piece of a leaf and apply the gel like substance directly onto your damaged skin - Leave blisters alone
The skin forms blisters to assist the healing process. Although bursting these is instinctive, it will decrease the healing ability as well as increase the chance for infection - Handle peeling skin with care
Resist speeding up the process by peeling the skin off before is ready. Rather let it come off naturally, but continue using the moisturising or healing creams to assist the skins natural healing power. The worst thing you can do for your skin is to irritate it by rubbing, scratching, or picking at it
Consult a doctor if badly sunburnt
Consulting a doctor is recommended if any of the following situations arise:
- High fever
- Large areas of the body covered in blisters
- Extreme pain. If you experience particularly painful burns then you may have to turn to an over-the-counter pain reliever
Prevention and/or Protection from Sunburn
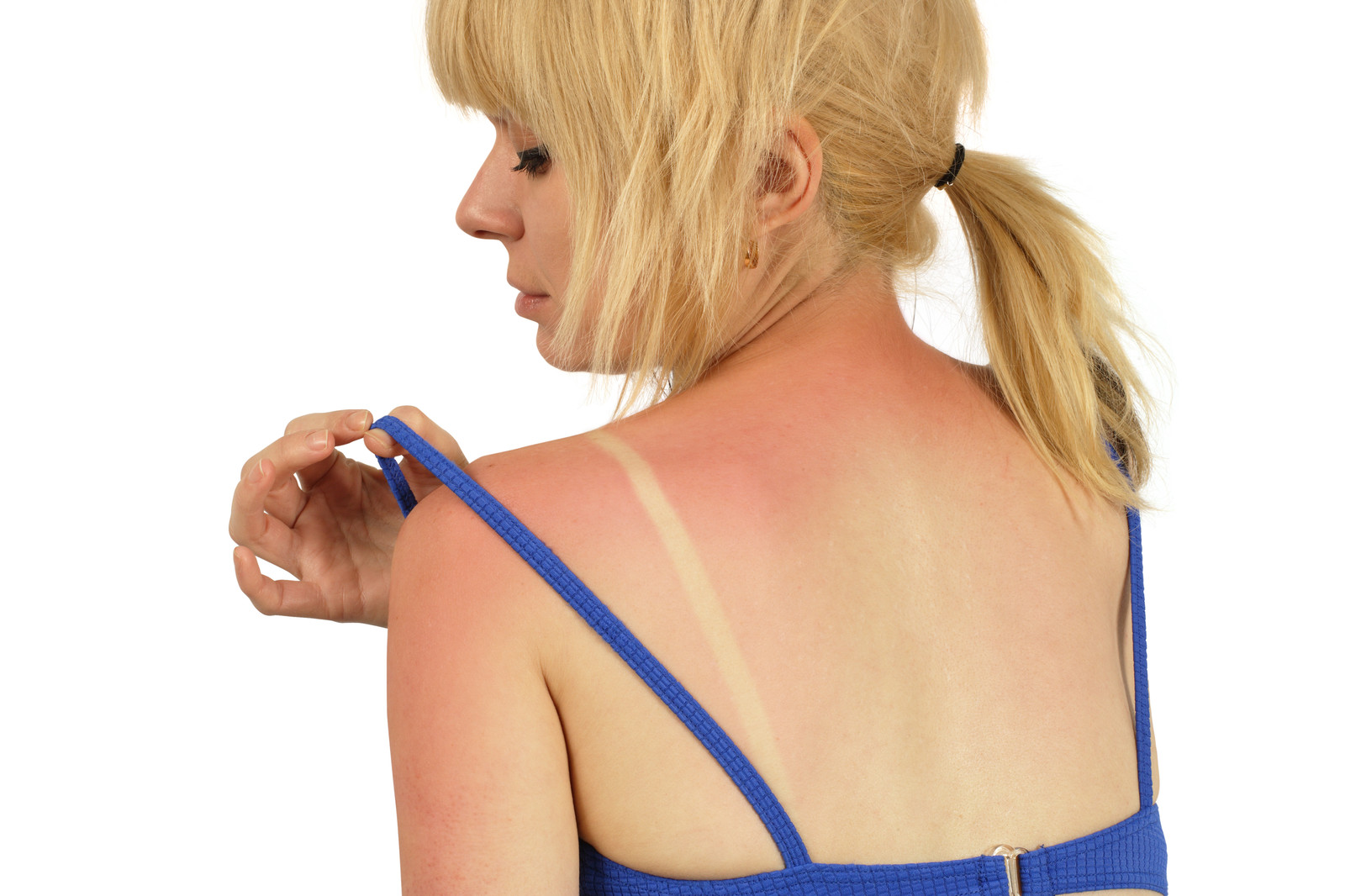

Treatment of any sunburn, never mind severe burns, is quite unnecessary if you make the right choice in protecting your skin upfront when exposed to the sun. Sunlight is extremely good for one's health and so if you know you'll be out in the sunlight for a while, take a few steps to keep sunburn from ruining your day by practicing good sun care.
You can prevent burning and the related skin conditions by protecting your skin whenever you're outdoors, even on cloudy days, by:
- Using a good quality sunscreen or sunblock to exposed areas of skin, not forgetting to apply it to areas that are often forgotten: ears, nose, back of the neck, feet, toes
- Wearing protective clothing such as hats, sarongs, and long-sleeve
- Controlled exposure when the sun is most potent - usually from 11 AM to 1 PM. Typically, this is when your shadow is shorter than you are. For your children, or more sensitive skins, reduce exposure to the sun particularly during the hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m
- Additionally, it is believed by some medical experts that eating the right foods can also help to protect you from sunburn. Everyday items such as oily fish like mackerel and herring, and fresh fruits and vegetables, contain substances which reduce the skin's sensitivity to the sun's harmful rays. Research projects in this line have produced some thought provoking results
Vitamin D and sunburn
This is rather an ironic situation, but studies have shown that if we have healthy levels of Vitamin D in our systems, it helps to alleviate sunburn symptoms. Ironic of course, because the best way to create healthy levels of Vitamin D in our systems is through direct exposure to the sun's UVB rays. One can choose to supplement with Vitamin D though.
The bottom line is always make sure to prevent sunburn in the first place!

Can Diet help with Sunburn?
Scientists are continually researching to understand what the most effective foods are to enable the skin's resistance to the sun, not as a substitute for sunscreen creams, but rather as an additional protective barrier. Thinking is predominantly focused around a diet of:
oily fish and fresh fruit and vegetables, providing vitamins and antioxidants
For example, a Dr Lesley Rhodes, consultant dermatologist and photobiologist at the Royal Liverpool University Hospital, carried out a study of fish oil. Omega-3, a polyunsaturated fatty acid, is abundant in fish oils and is believed to act as an internal sunscreen against sunburn and light-sensitive rashes.
Dr Rhodes conducted a series of tests with a number of volunteers to measure burns caused by ultraviolet light on small areas of their skin. Then they were given the equivalent of 2 plates of oily fish a day, contained in Omega-3 capsules, for a period of 3 months. Subsequently, the repeated exposure to ultraviolet light caused significantly less sunburn.




New! Comments
Have your say... please leave me a comment in the box below.