Effects of tanning on your skin
The effects of tanning on your skin and your overall health are worth knowing - whether you go to a tanning salon, down to the beach, by the pool or outdoors anywhere.
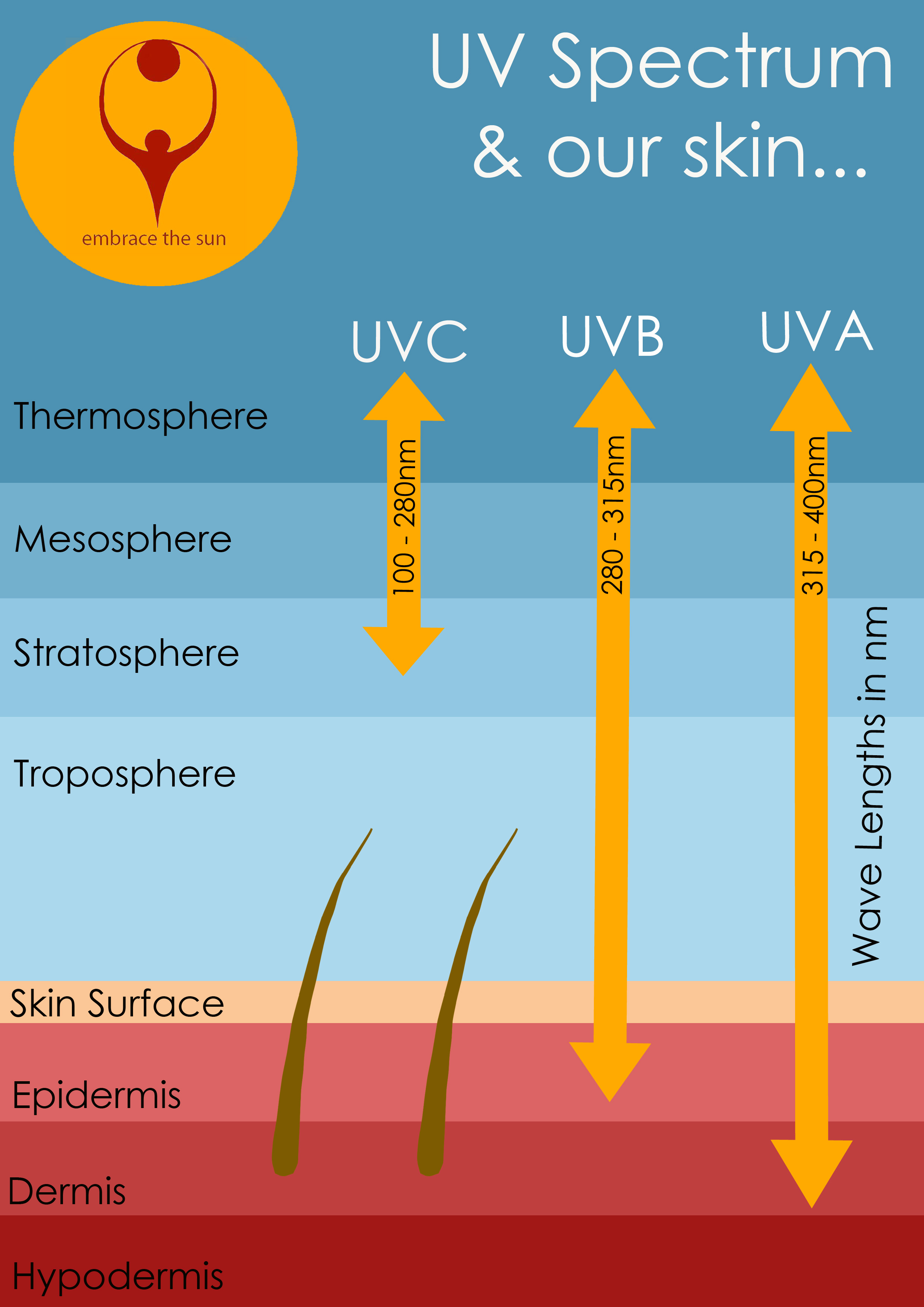 Effects of tanning on your skin
Effects of tanning on your skinAs soon as the sun starts to shine, the outdoors beckon and off everyone goes, to get that wonderfully alluring tanned, bronzed and healthy looking skin.
When that heat wave arrives, everyone's out there sun tanning. Both teens and adults alike crave that sun kissed look.
Looking at the reality of it all, there are both positive and negative effects of tanning.
Exposing your skin to the UVB rays of the sun allows a photosynthesis like process to happen whereby your skin creates Vitamin D.
This is a very natural process that boosts our bodies' own defensive abilities to overcome many things, including skin cancer as well as other cancers.
Vitamin D - a side effect of tanning
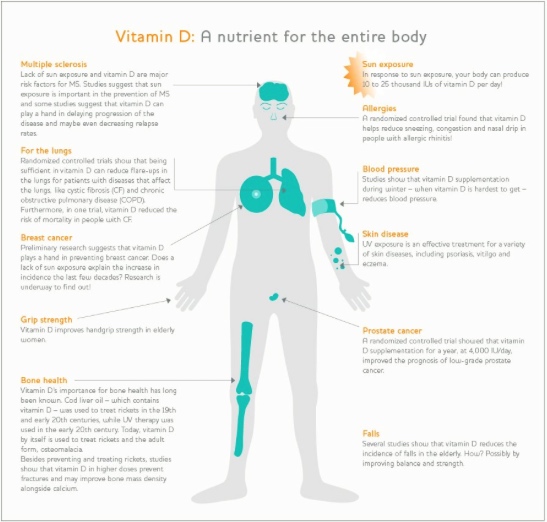
However, overexposure will result in the skin getting burnt and this is likely to start a process that culminates in skin cancer. So, for ultimate health benefits, it's very important to manage your time in the sun so as not to burn!
The more you understand about the effects of overdoing your sun exposure, the more likely it is you will practice good sun care habits that include:
- Applying heathy, non-toxic sunscreen
- Wearing protective clothing
- Managing your time in the sun
Melanin increase as an effect of tanning
 Pale skin types with little melanin
Pale skin types with little melaninThe skin contains a substance known as melanin. This substance on its own is responsible for the natural color of your skin, the one you are born with. The more melanin someone has in their system, the darker their skin will be.
So, one of the key side effects of tanning is that your skin creates more melanin, which is what darkens your skin color. The more you are exposed to the sun's UV rays, the more melanin will be created and gradually your skin will change color. The reverse applies too - as you stay away from the sun, the melanin will slowly decrease back to the color you were born with.
There are a number of tanning products that work inside the body to increase the production of melanin, which can result in a deep, rich and natural looking tan without the need for exposure to ultraviolet rays.
These are mostly known as tanning accelerators, which often come in a lotion or pill form, designed to stimulate production of melanin within the body.
Sunburn & skin cancer : side effects of tanning
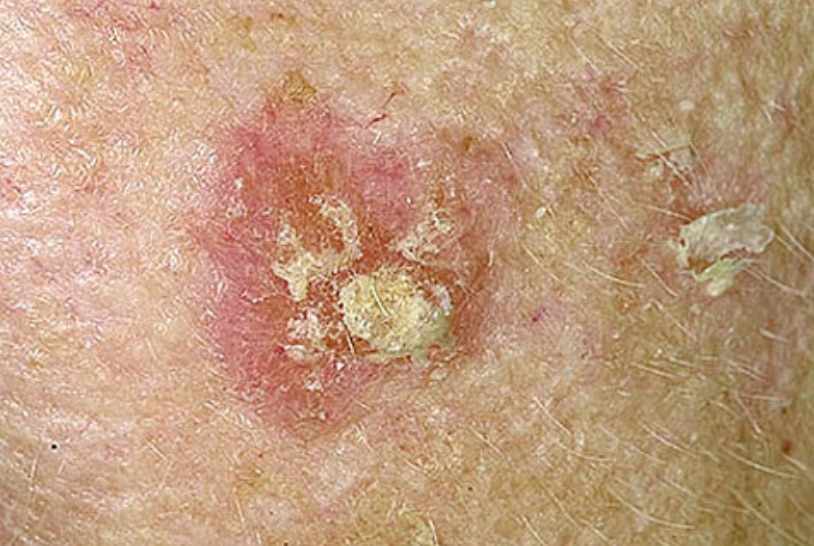 Squamous cell carcinoma skin cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma skin cancerAs mentioned, sunburn is another of the main effects of tanning. When you get sunburned, your skin's DNA is likely to have been affected and this is what then leads to skin cancer.
At best, the skin is sore to the touch, red, and inflamed. At worst, it blisters and peels immediately, but mostly, after a few days the skin of the sunburned area will begin to peel off.
While there are millions of people each year that do get sunburnt and don't really care much, it is critical to know that with each case of sunburn, you potentially put yourself at risk for developing skin cancers. Some are more life threatening than others, but all are extremely unhealthy.
The most deadly form is melanoma and if not diagnosed and treated early, it can be fatal. However, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common forms of skin cancer that occur from overdoing sun exposure.
They are a very negative effect of too much tanning. They are certainly not pleasant to look at and invariably result in surgery to remove them.
Effects of tanning on your eyes
 Sunglasses for eye safety when tanning
Sunglasses for eye safety when tanningThere is a lot of information about the dangers of tanning and UV skin exposure, but it is easy to forget that the eyes are exposed as well.
Tanning can cause problems with your eyes, especially when using tanning beds. Usually, your eyelids or ordinary sunglasses are enough protection for your eyes, but there are several problems that can be caused through over exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays:
- Pterygium - an overgrowth of the conjunctiva, which is the clear tissue that covers the white of your eye. Usually a non-cancerous condition, it is most commonly obtained by people working outdoors, or by those exposed to a lot of wind and sun. It can grow big enough to block your vision, and while it can be removed surgically, it may grow back. A pterygium does not usually require treatment.
- Cataract - is a clouding over the eye lens. Cataracts are the leading cause of blindness worldwide and are sometimes caused by over exposure to UV rays. The vision becomes blurred when the lens cloud, which can also cause double vision, and especially at night, unbearable glare from lights. Treatment required is usually by surgery.
- Ocular melanoma - is basically cancer in your eye. Just like the skin cancer melanoma, except in your eye. Although not common at all, it is the most common primary eye cancer. Ie. It starts in your eye. Other cancers of the eye typically arrive from somewhere else, having spread to your eye. So the effects of tanning, or the over exposure to UV rays, is logically considered to be a key risk factor for ocular melanoma, although it is not yet scientifically proven.
So, for better eye protection, wear wide-brimmed hats and quality sunglasses that contain both UVA and UVB protection.




New! Comments
Have your say... please leave me a comment in the box below.