Vitamin D deficiency treatment
Increasingly, people around the globe require Vitamin D deficiency treatment as the deficiency seems to be found in people of all ages, sexes, cultures or geographical locations.
 Vitamin D deficiency treatment outdoors in the sunshine
Vitamin D deficiency treatment outdoors in the sunshineKnown as the "sunshine vitamin", vitamin D is very efficiently produced by the body through our largest organ - the skin - in response to direct exposure to the UVB rays from the sun.
There are multiple causes of vitamin d deficiency and depending on your circumstances, daily exposure to the sun's rays and/or supplementation may be required for treatment.
Vitamin D Deficiency treatment for potential causes
You may find some of the following causes of vitamin d deficiency apply to yourself. A Vitamin D deficiency treatment may be required, should you find more than one is applicable.
- Limited sun exposure
This can be complicated by variances in skin type, geographical position, sun sensitivities, excessive use of sunscreen or cultural clothing requirements - Diet inefficiencies or Malnutrition
This could decrease your Vitamin D processing capabilities - Overweight
When overweight, Vitamin D is stored in our fat and not made available to our bodies - Gastrointestinal diseases
If you have pancreatitis, bowel disease, amyloidosis or celiac disease, they will complicate your ability to absorb Vitamin D - Hepatic disease
Liver disease or some of the anti-epileptic medications, can create complications for Vitamin D processing - Renal disease
Any natural ageing, kidney inefficiencies or Nephrotic syndrome could create difficulties processing Vitamin D
The best way to establish whether or not you actually have a deficiency is through a blood test.
Depending on which vitamin D deficiency treatment program you may subscribe to, use the test results as your base from which to monitor and improve.
Sun exposure - best Vitamin D deficiency treatment?
 Get your Vitamin D directly from the sun
Get your Vitamin D directly from the sunThe most efficient Vitamin D deficiency treatment is through full exposure to the sun when it is most direct, while unprotected by either sunscreen or shade or clothing.
At any time that your shadow is longer than you are, you are sure to obtain no vitamin D benefit at all. When it is directly overhead, (should you be lucky enough to live in a geographical location where the sun moves directly overhead), it is the best possible time.
However, as always, it is paramount that you do not get sun burnt. Balance is key.
How to know of you are getting Enough Vitamin D from Sun Exposure
Too much sun will cause your skin to burn and that is what you must avoid at all costs. Just enough every day is optimal to provide Vitamin D.
But how do you know what 'just enough' is?
The time required while exposed to the sun's UVB rays is further complicated by your skin type. The darker your skin, the more direct sunshine is required to create, or synthesise Vitamin D.
The less melanin, or the paler your skin, the easiest it is to make Vitamin D. So the more 'tanned' your skin becomes, the higher the melanin content will be and therefore, more time will be required to create the Vitamin D.
If increased sun exposure is not possible for any of the reasons below, your Vit D deficiency treatment may have to include supplementation:
- limited direct sun exposure available, by being in an inconvenient location
- having a dark skin type that requires more time in the sun than you have available
- being sun sensitive for any number of reasons, including certain medication
- always wearing full body cover clothing whenever outdoors
Supplementation in vitamin D deficiency treatment
 Vitamin D supplementation
Vitamin D supplementationThere are many patients and medical practitioners that believe that enough vitamin D can be obtained through their diet and no supplementation is required in any sort of Vitamin D deficiency treatment.
This is true in some cases where people eat a lot of fatty fish. However, most food contains relatively low vitamin D, including Vitamin D fortified foods like cereals and dairy products.
Vitamin D supplementation is safe and inexpensive, yet vitamin D deficiency often remains undiagnosed or is under treated. Over the past 15 - 20 years, more than 10,000 studies on vitamin D have been published in various research journals.
The results show that:
- Increasingly more vitamin D is required than previously thought
- City lifestyles have reduced our daily exposure to sunlight dramatically
- Vitamin D deficiency is far more prevalent than previously estimated
- Vitamin D deficiency treatment requires far more than a standard diet can provide
Vitamin D insufficiency generally refers to a blood level of hydroxyvitamin D below 30 ng/mL, while Vitamin D deficiency refers to a blood level below 20 ng/mL.
However, these levels are no longer relevant for determining the amount of vitamin D required for optimal vitamin D treatment.
UVB Map: Illustrating global access to healthy UVB levels
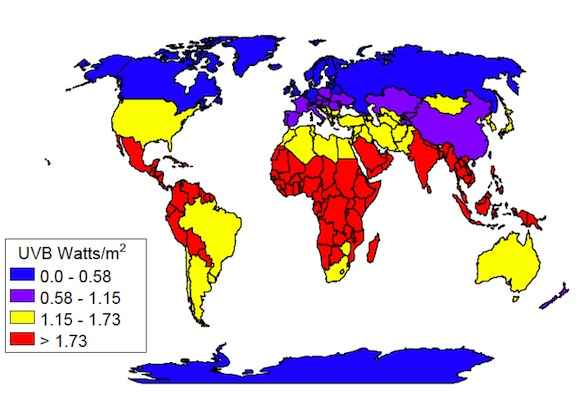
Now that so many health organisations and professionals realise that our blood requires higher levels of vitamin D, it has also been acknowledged that it takes higher levels of vitamin D supplementation to bring blood levels up to what is considered a healthy standard in any Vitamin D deficiency treatment program.
Examples are:
- Where sunlight is limited, at least 1,000 IU daily of vitamin D are needed to increase blood levels of vitamin D from 20ng/mL to 30 ng/mL or higher.
- A minimum of 700 IU is needed to prevent bone loss for those with any risk for osteoporosis
- Levels of intake below 400 IU have not demonstrated any prevention results
- Where there are autoimmune issues like rheumatoid arthritis or multiple sclerosis, supplemental doses of vitamin D range in the 1,000s or more likely in the 10,000s of IUs.
For many people, the best way to get enough vitamin D is by taking a supplement.
However, the level in most multivitamins is too low at around 400 IU, though many are now increasing this to 2,000 IU of vitamin D or more. If your multivitamin has less than 2,000 IU of vitamin D, you should consider adding a separate vitamin D supplement.
If you are sitting with an extreme deficiency or some sort of health disorder or osteoporosis risks, it is advisable to take at least 5000 IU's daily. The key is to get your Vitamin D level (25(OH)D2, 25(OH)D3, or total 25(OH)D) blood levels up to an acceptable level and this should be a lot higher if you are wanting to boost your body's immunity capabilities.
How much supplementation is enough for a Vit D deficiency treatment program?

As one of the safest substances known to man, vitamin D toxicity is very rare. In fact, people are at far greater risk of vitamin D deficiency than they are of vitamin D toxicity.
The Harvard School of Public Health, together with many other health organisations, recommend supplementing with vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) rather than D2 (ergocalciferol or pre-vitamin D). A key reason provided is that Vitamin D3 is chemically indistinguishable from the form of vitamin D produced in the body after exposure to the sun.
Both D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol) are available as dietary supplements. A single dose of 50,000 IU of D2 or D3 produces a similar increase in the total 25(OH)D concentration, but the apparent longer half-life of D3 suggests that less frequent dosing may be needed. One situation in which D2 may be preferred is a vegetarian or vegan diet. It is recommended that both D2 and D3 be taken with a meal containing fat to ensure maximum or optimal absorption.
Since 1997, the Food and Nutrition Board in the USA advised a Average Intake (AI) of vitamin D of 200 to 600 IU/d. This AI was intended to provide for the needs of all individuals, but without absolute certainty from the data provided at that time, they were cautious. This daily recommended amount has steadily risen since then by all sorts of organisations, including the Institute of Medicine, so it can be very confusing as to how much supplementation one can take.
How much vitamin D is needed for treatment of severe vitamin D deficiency - considered by most to be <10 ng/mL? Although not validated by clinical trials, a commonly applied strategy is to prescribe a "loading dose" (eg, 70,000 IU of vitamin D orally once weekly for 2-3 months, or 3 times weekly for 1 month). A review of multiple loading algorithms suggested that a minimum total dose of 600,000 IU best predicted an end-of-treatment 25(OH)D level greater than 30 ng/mL. Depending on what you wish your end-of-treatment level to be, this total can be increased.
A maintenance dose averaging 4000 IU/d meets the current safe upper limit guidelines and is well below safe upper limits reported by others.
Vitamin D absorption problems?
Patients with malabsorption often require larger amounts in any vitamin D deficiency treatment program, or for a maintenance dosing of vitamin D.
An example are patients with gastric bypass procedure malabsorption issues, where they could require 50,000 IU as a maintenance dose once weekly or as frequently as daily to maintain sufficient levels.
In extreme malabsorption situations, the most effective vitamin D deficiency treatment is UVB exposure - either through direct sunlight or phototherapy indoors.
Additional cofactors required for
Vitamin D Deficiency treatment

If taking an oral supplement of vitamin D, you must be aware of the need for extra supplements. Vitamin D has many cofactors, but the ones below are the vital ones, where magnesium is the most important one of all.
Magnesium
Dr Cannell from the Vitamin D Council has said that "Severe magnesium deficiencies severely impair vitamin D's ability to work. What is not known, is how mild to moderate magnesium deficiencies will affect vitamin D metabolism.
The safe thing to do is to eat green leafy vegetables and a handful of sunflower seeds and nuts every day or take a vitamin D supplement with added magnesium."
Vitamin K
Natural Medicine Expert, Dr. Kate Rheaume-Bleue explained:
"When you take vitamin D, your body creates more vitamin K2-dependent proteins, the proteins that will move calcium around. They have a lot of potential health benefits, but until the K2 comes in to activate those proteins, the benefits aren't realised. So, really, if you're taking vitamin D, you're creating an increased demand for K2. And vitamin D and K2 work together to strengthen your bones and improve your heart health."
Unless you're eating good quality butter, cheese, grass-fed meats or natto (fermented soybean food popular in Japan), you will need a supplement.
Zinc
The base of the fingers of the Vitamin D Receptor each contains a zinc molecule.
Boron
Boron is involved in the rapid, non-genomic action of Vitamin D on the cell wall.
The wisest thing to do, urges Dr Cannell, is to eat green leafy vegetables and a handful of seeds every day as this combination contains all the co-factors Vitamin D needs.
Vitamin D deficiency treatment references:
NCBI how to prevent and treat Vitamin D deficiency
Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266-281
Vitamin D Council: Magnesium and vitamin D's co-factors



