25 hydroxy vitamin d
25 hydroxy vitamin D is one if the several forms of vitamin D3, which of course is the more common term referred to when talking about the 'newly' discovered health properties of this vitamin.
As scientists discover more and more about it's remarkable health giving properties, so we learn more and more of its incredible value in our lives.
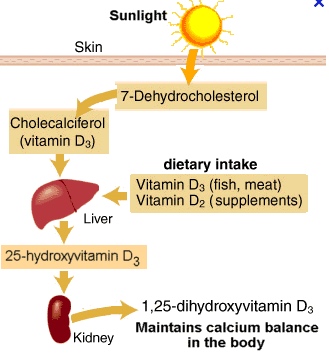 25 hydroxy vitamin D process, or Vitamin D3, process within the body
25 hydroxy vitamin D process, or Vitamin D3, process within the bodyIts abbreviated name is 25(OH)D or 25 oh vitamin d and is what many publications will refer to. The vitamin D3, produced by our bodies through our skin and UVB rays, undergoes an hydroxylation process in the liver with the enzyme cholecalciferol 25-hydroxylase and the end result is the prehormone called 25 hydroxy vitamin D3.
This in turn is converted by the kidneys into 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, or calcitriol, which is called a secosteroid hormone and is the active form of Vitamin D3.
Cholecalciferol is an inactive, un-hydroxylated form of vitamin D3 created in our skin via the sun's UVB rays
25 hydroxy vitamin D, also called calcifediol, calcidiol, or hydroxycholecalciferol, is one of the forms measured in our blood to assess the status of our vitamin D
25 hydroxy vitamin D blood tests
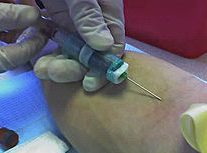 Typical Vitamin D blood test
Typical Vitamin D blood testIn order to test whether you have too much or too little vitamin D in your blood, the 25-hydroxy vitamin D test (or 25 oh vitamin d test) is the most accurate way to measure this.
This is done through an ordinary blood sample test where the blood is drawn from a vein.
Results are considered normal with anything measuring from 30.0 to 74.0 nanograms per milliliter but the interpretation of these results tend to differ from one country to another, or one medical practitioner to another.
One really needs to consult with a medical practitioner about any specific significance in your results with respect to your overall health status.
25 hydroxy vitamin D Results too low?
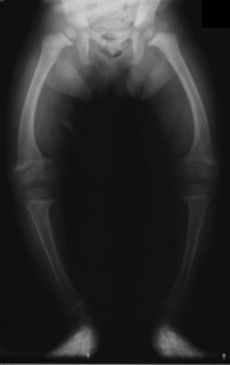 Rickets - caused by low Vitamin D3
Rickets - caused by low Vitamin D3A vitamin D deficiency will be suggested with lower than normal results. This can point to many different causes:
- Insufficient exposure to the sun's UVB rays
- Diet inadequacies of foods high in vitamin D
- Evidence of diseases of the liver or kidney
- Disorders that reduce the digestion or absorption of fats will make it more difficult for vitamin D to be absorbed into the body.
- Possible interference from certain medicines like phenytoin, phenobarbital, or rifampin
Low 25 hydroxy vitamin D results are often seen in African-American children where they are denied enough exposure to sunlight. This is especially evident in the winter and the higher latitudes, but is also seen increasingly in infants who are exclusively breast fed by mothers lacking in vitamin D3.
As vitamin D3 helps the body to control calcium and phosphate levels, if you have a deficiency this can lead to Rickets.
Also, low vitamin D levels in babies or infants is commonly misdiagnosed as physical child abuse as their bones break so easily. In some heart-rending situations, children are removed from their parents without any vitamin D tests having been considered first.
The Vitamin D council believe American newborns should have routine 25 hydroxy vitamin D tests in recognition of the multitude of afflicted infants. Even if they are on formula and not just being breast fed, 12 months later if weaned onto anything other than cows milk the deficiency will show itself in things such as Rickets or even Autism.
An increased risk of developing cancer has also been claimed with low 25 hydroxy vitamin D test results. According to John Hopkins Children's Centre "Recent studies have found a link between low vitamin D levels and some cancers, heart disease, suppressed immunity and even premature death." Although vitamin D deficiency is not seen as the cause of these disorders, it is seen as a powerful enabler to assist the body in its healing process.
25 hydroxy vitamin D results too high?
 Embrace the sun, Embrace Vitamin D
Embrace the sun, Embrace Vitamin DHigher than normal levels of Vitamin D suggesting an excess, can create a condition called hypervitaminosis D.
With an excess of vitamin D in your system, abnormally high levels of calcium in the blood can result. This can in turn severely damage your bones, soft tissues, or kidneys over a period of time.
Typically this is caused by pharmaceutical over-supplementation rather than a diet rich in vitamin D as levels of vitamin D in foods are relatively low in comparison to the supplements.
It is also not possible to obtain a toxic level of vitamin D through exposure of your skin to the sun's UVB rays.
Why order a 25 hydroxy vitamin D test?
These are some of the numerous situations whereby you may be required to submit blood for a vitamin D test:
- calcium levels are low
- bone malformation in children or evidence of Rickets
- infants bones breaking too easily
- bone weakness or softness
- fracture in adults and indications of osteomalacia
Some medical conditions cannot absorb vitamin D very well and so will require monitoring of the vitamin D levels. Examples are:
- Cystic fibrosis
- Crohn's disease
- Patients with gastric bypass surgery
Due to the increased level of research and scientific work being done on Vitamin D, deficiency is thought to be much more prevalent than believed just 10 years ago. eg. Some studies have shown that as many of 50% of the elderly and women being treated for osteoporosis may be Vitamin D deficient.
A 25-hydroxyvitamin D test is now most often ordered prior to anyone starting drug therapy for osteoporosis. Some osteoporosis medications even include the recommended Vitamin D dose but the amount varies and is still under debate as to what is correct.
References:
Weng FL, Shults J, Leonard MB, Stallings VA, Zemel BS. Risk factors for low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in otherwise healthy children and adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86(1):150-158.
Lappe JM, Travers-Gustafson D, Davies KM, Recker RR, Heaney RP. Vitamin D and calcium supplementation reduces cancer risk: results of a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;85(6):1586-1591.
Specker BL, Valanis B, Hertzberg V, Edwards N, Tsang RC. Sunshine exposure and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in exclusively breast-fed infants. J Pediatr 1985;107(3):372-376.




New! Comments
Have your say... please leave me a comment in the box below.